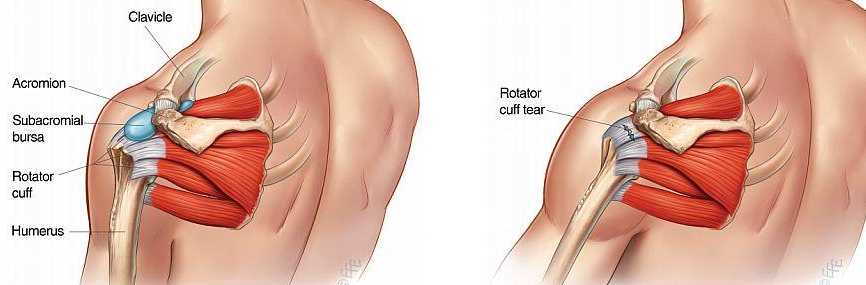
What is rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround the shoulder joint. They provide power for motion at the shoulder joint in various directions, and also help in maintaining the ball of the upper arm bone firmly within the shallow socket of the shoulder joint.
What are rotator cuff tears, and how do they occur?
Rotator cuff tears are a common source of shoulder pain and disability among adults, significantly affecting one’s quality of life and ability to perform everyday activities. A rotator cuff tear may occur due to an acute injury, or, more commonly, it results from gradual wear and tear, multiple subtle overuse injuries, or age-related degeneration, over time.
Symptoms often include pain and weakness of varying extents. Many a times, pain is present at rest and at night, particularly if lying on the affected shoulder. Pain and weakness makes ordinary activities difficult like combing hair or lifting jars or files from an overhead shelf.
What are the treatment options for rotator cuff tear?
Treatment is required if the rotator cuff tear is causing symptoms.
Understanding the treatment options available can empower patients to make informed decisions regarding their health.
Treatment of rotator cuff tears depends on many factors. Some of these factors are the extent of patient’s symptoms, age group, physical demands, duration of tear, condition of the shoulder joint surfaces, health of the torn muscle and tendon, fatty changes in the muscle, duration of rehabilitative treatment, and response to various treatment strategies like injections etc. Treatment also depends on which muscle tendons are torn, whether a particular tendon is affected along its whole attachment from front to back or part of it is involved, and whether the full thickness of the tendon is torn or the tear is partial thickness. These are some of the many factors that your treating arthroscopic surgeon will take into consideration before suggesting the best suitable treatment plan for you.
Can rotator cuff tears be managed without surgery?
In many cases, non-surgical treatment options can provide pain relief and improve the function of the shoulder. These may include:
Physiotherapy: Physical therapy with focused exercises can strengthen the muscles around the shoulder, making it more stable and relieving pain. In addition, there are various electrotherapy modalities (part of physiotherapy) like IFT, TENS, NMES, local ultrasonics, etc that can be added to provide relief.
Medications: A short course of anti-inflammatory medicines can reduce pain and swelling. However, prolonged regular use is not recommended due to side effects of medicines.
Steroid Injections in the shoulder: Steroid is a powerful anti-inflammatory agent that can be injected into the shoulder around the rotator cuff to relieve pain and swelling. In some patients, this gives considerable and long-lasting relief. However, in others, significant relief may not occur or it may be temporary. Multiple steroid injections should be avoided as they may have a deleterious effect on the condition of the rotator cuff.
It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.
What are the surgical options for rotator cuff tear?
Surgery is considered if non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief. The type of surgery depends on the size, shape, and location of the tear, tissue quality, as well as the patient’s lifestyle and age. Common procedures include:
Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: The torn portion of the cuff is repaired back to the bone using special anchor devices through arthroscopic surgery (key-hole surgery). The surgeon makes small incisions and uses a camera and instruments to repair the tear.
The configuration of repair and the number of anchors required depends on the tear size and shape as well as how old the tear is. Generally, a “double-row repair” can be performed which provides a better seating of the tendon on the bone. In some instances, a single-row repair suffices, and in some instances, the tissue retraction makes it impossible to achieve a double-row repair, and in such cases, your surgeon may decide to do a single-row repair. If the tendons are too retracted and adherent, procedures like single interval slide or double interval slide may have to be added in order to obtain reduction.
Arthroscope-assisted tendon transfer: For an experienced arthroscopic surgeon, majority of cuff tears can be repaired after single or double interval slides. However, there are some cases with massive irreparable cuff tears. In such cases, if the joint is not too damaged, then procedures called “tendon transfers’ can be done to improve the shoulder function. One of these is “lower trapezius transfer with autologous hamstring”. Part of this procedure is done using key-hole surgery, and a part of it requires a small incision. It is a straightforward procedure for an experienced arthroscopic surgeon, that can provide a reasonable improvement in shoulder function.
Reverse shoulder replacement: If the joint is already damaged along with a massive cuff tear, then damaged parts of the shoulder joint are replaced with artificial components (joint replacement). In such cases, a special type of artificial joint is used called “reverse shoulder arthroplasty”.
Your treating arthroscopic surgeon will be in the best position to advise a suitable treatment option in your particular case. Many a time, the decision regarding treatment options needs to be taken during surgery after inspecting the cuff tissue.
Post-Surgery rehabilitation:
Surgery is only a part of the treatment, and post-operative rehabilitation is as important as the actual surgery. Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in recovery, focusing on gradually regaining shoulder strength and flexibility. Recovery times can vary based on the type of surgery performed and individual patient factors, but may extend from 4 to 9 months. Many patients experience significant improvement in function and reduction in pain following the surgery and rehabilitation process.
Living with a Rotator Cuff Tear:
Managing a rotator cuff tear involves patience, commitment to rehabilitation, and closely following medical advice. While treatment can significantly improve symptoms, it is also important for patients to adjust their activities to avoid actions that may exacerbate the condition. With appropriate care, most individuals can return to their normal activities with improved shoulder function and reduced pain.
In conclusion, a rotator cuff tear, while potentially debilitating, does not signify the end of an active lifestyle. Through a combination of medical treatment, physical therapy, and surgery, patients can achieve significant relief from symptoms and regain much of their shoulder’s function. It is essential for patients to discuss their symptoms and treatment options with their arthroscopic surgeon to devise a plan that best suits their individual needs and goals.

Dr. Himanshu Gupta
MBBS (AIIMS Delhi), MS Ortho (AIIMS Delhi)
Senior Consultant Sports Injury and Sports Medicine Specialist
(Arthroscopy and Joint Replacement)